“How Soon is Soon Enough ?”
Since the days of Koch’s Postulate, isolation and culture of a pathogen has become the corner stone of diagnosis of an Infectious disease. In 1930s, Alexander Fleming discovered Penicillin and triggered the Era of Antibiotics. Since then allopathic system of medicine has become the main stream of treatment all over our world. All other systems of cure has been thrown into a common pool of Alternative Systems.
Growing a Pathogen from the blood culture of an Infectious case still remains the Gold Standard for diagnosis and Evidence Based Treatment.
It has one downside though.
It takes time.
The microbiologist would take few ml of blood from a sick baby, incubate it overnight in a nutrient media to allow the pathogen to grow lusciously. From this non specific growth, sub cultures are grown into selective agar plates where colonies are formed. These growth are then Gram stained and examined under microscope. Accordingly, we can identify the culprit as either a Gram Positive Cocci (GPC: say Staphylococci) or a Gram Negative Bacilli ie. E Coli. ( GNB) or a Fungal filament and so on. This can give us a broad view to select our antibiotics.
Antibiotic Susceptibility Test ( AST)
Broad spectrum antibiotics are a nuisance. So we have refined it further into Antibiotic Susceptibility Test.
The culture was further seeded into selective antibiotic impregnated plates to determine their drug susceptibility. Early doctors were able to do miracles by one dose of appropriate antibiotics. Culture and Sensitivity is the major difference between Allopathic System and all other systems of treatment.
But this takes still more time.
These technique can’t identify viruses in the baby. Viruses cannot be stained or seen under a microscope. They are the simplest thing on tis earth. A Code and two proteins. The Code consists of molecules like RNA or DNA.
Still this method of culture helped us to treat the infections so effectively that Microbiology became a full scale new speciality. Their job description was a crisp one liner-
They said: this will take time. And if you want to know which antibiotics to choose that will take still more time.( 4-5 days)
But the paediatricians are an impatient lot. So they demanded let’s have the result in hours not in days.
Now the job description is extended with one more word but in Capitals :
So the Microbiology people tinkered their incubation chamber with sensors and softwares. The Bactec and Bact/Alert systems can indicate us a positive growth in hours. But for identification of the organism we still have to stain them with Gram stein. We must seed them in an antibiotic impregnated plate to study AST. But then..
How soon is acceptable ?
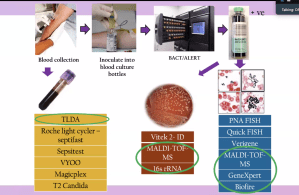
This has led to development of a radically different speciality that can identify the microbe both from the culture plate as well as from an EDTA-Whole blood sample. It’s known as molecular biology.
Life on our earth runs on proteins. Enzymes, Hormones, rhodopsin in our eye, Hemoglobins, Myoglobins all are proteins. Each microbe has some signature protein. Even the antibiotic resistance of bacteria are mediated by selective proteins like MecA ( Methicillin resistance) Carbapenemase or Van A, Van B ( Vancomycin resistance) secreted by the culprit. Identification of all these proteins is known as Proteomics. This is something like identifying the salts in our inorganic Classes by the colour they produce in a flame.
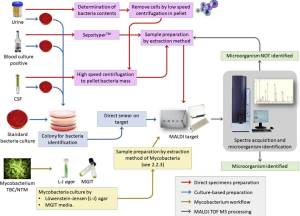
Mass Spectrometry is a technique by which each and every protein can be separated and identified in the physics lab just like we separate HbA from HbF and HbS in an electrophoresis plate. This is instantaneous.
MALDI TOF MS is an instrument which separates and identify every organism, antibiotic resistance by identifying their complex protein in less than an hour time. Now we don’t have to wait for days to sub culture the bacteria and study their morphology or gram stained slides.
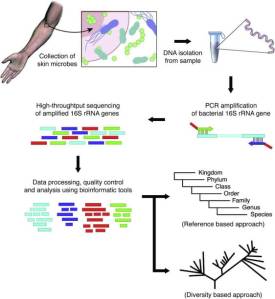
Each protein is characterised by its unique genetic code: an unique strand of DNA or RNA. Identifying the sequence of the nucleic acid can identify the protein 100%. This is done by two methods:
- PCR: The bacterium cell is lysed, its nucleic acid content is extracted and is identified by dedicated Probes. As this is a multiplier technique, the nucleic acid content can be multiplied on and on through successive Cycles and very minute quantities of DNA/RNA can be identified. This takes less tha 6 hours. al, the steps of this process has been compacted into a cartridge with advanced software. So that a Genexpert on our lab shelf can display the result in 6 hours just like that.
Downside : One probe can read only one code.
Multiplex PCR: Now we have developed PCR readers that can read several microbes from a single sample. Roche’s Septifast and Sepsitest, Vyoo, Magicplex, Biofire are all Multiplex PCR systems. Advantage: These tests can be done on whole EDTA blood. No need of incubation and culture.
- Vitek 2 ID cards have further made it doctor friendly by incorporating the multiplex PCR on a card.
- Sanger’s Sequencing: Frederick Sanger has won the 1958 Nobel prize for his discovery of the structure of Insulin. He refined his technique to sequence each and every DNA/RNA to receive his second Nobel in 1980. Now we can sequence the Nuceic acid content of any organic sample by Sanger’s Sequencing. *Verigene* uses Sanger’s sequencing to fully decode the genetic code of a pathogen in the sample. Otherwise we can identify
- 16 subunit Ribosomal RNA is known as the universal PCR. It can tell us if a Prokaryote is present in the human blood sample. An essential step to establish sepsis in a newborn without identifying the cause.
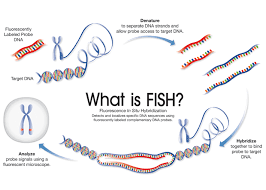
These are Elisa like tests where wells are impregnated with Fluorescent tagged hybrid probes. When the fresh culture from a Bactec is charged the sample lights up if the microbe is present. Downside: Unlike PCRs it lacks multiplier effect. However it serves a good purpose in several fields like cancer cytology.
Today, we can assess a septic newborn within hours of sampling by combining Molecular biology and Microbiology.
Is that soon enough ?